The Stats in Social Work-Why the numbers matter?
- carolynwaller
- Feb 11, 2023
- 5 min read
The Society for Social Work and Research is determined to advance social work research in all spheres of life. The organization's focus is to design and transfer rigorous research practices that influence policy decisions that impact social welfare programs. Therefore, explaining the role statistics plays in social work and the relevance of outliers in contextualizing different phenomena is vital. The advancement of social sciences and the resolution of society's challenges lies in using scientifically robust statistical techniques to develop effective programs and evidence-based policies.
The degree to which a discipline applies statistical tools impacts its epistemic and scientific development. Statistics are essential in social work because they provide a measure of evidence for a specific hypothesis, or as Dunleavy and Lacasse (2021) point out, they “provide a measure of fit for competing models” (p. 1). When statistics are not applied in social work, practitioners risk proposing or delivering policies and interventions that are of little benefit to clients because they have yet to be empirically evaluated for effectiveness. Statistics are important because they allow social scientists to critique empirical research, evaluate practice, and disseminate research. Using numerical evidence to reach meaningful conclusions is essential in the field of social work. The ability to analyze claims based on quantitative evidence is a crucial skill since it allows practitioners to differentiate between dubious and reasonable assertions.
The usefulness of statistics is demonstrated in the analysis of various forms of information. All social sciences rely on accurate results to inform decisions in different contexts. Statistics help practitioners navigate the pitfalls associated with assessing large quantities of data. For instance, individuals are equipped with the skills to identify biased samples, overgeneralization, and incorrect analyses. It is vital to ascertain the accuracy of the information to avoid making wrong decisions or proposing ineffective interventions.
The view that statistics are essential in the field of social sciences is based on empirical research findings. Dunleavy and Lacasse (2021) demonstrate the applications and relevance of various statistical principles in social work. The researchers highlight the centrality of statistics in the social sciences by providing a nuanced description of relevant concepts and their applications. Contemporary society and the challenges they present are best understood through the evaluation of quantitative data. Therefore, all practitioners in the field of social sciences must be equipped with essential statistical skills to make sense of the intricacies that characterize modern society.
Researchers must choose the most effective technique to apply in the analysis of specific datasets. The process of assessing the data for errors or test assumptions often involves decisions regarding handling outliers. Leys et al. (2019) note that the choice a researcher makes regarding managing outliers leads to the creation of different datasets that may ultimately alter the study's outcome. The failure to detect and address outliers may create inaccuracies in statistical analyses and reduce the external validity of the study’s results (Mowbray et al., 2019). Outliers are best described as " extremely distant from most of the other data points" (Leys et al., 2019, p. 1). It is often the case that outliers cause a problematic influence on the development of substantive assessments of the associations between variables. Despite the challenges mentioned above, outliers should be included in the results. This is because careful examination of these data points may result in the generation of new theoretical insights that form the foundations for future studies. Figure 1 below demonstrates outliers in a histogram and boxplot of the frequency distribution of age among frontline nurses.
Figure 1
Histogram and boxplot of the frequency distribution of age among frontline nurses
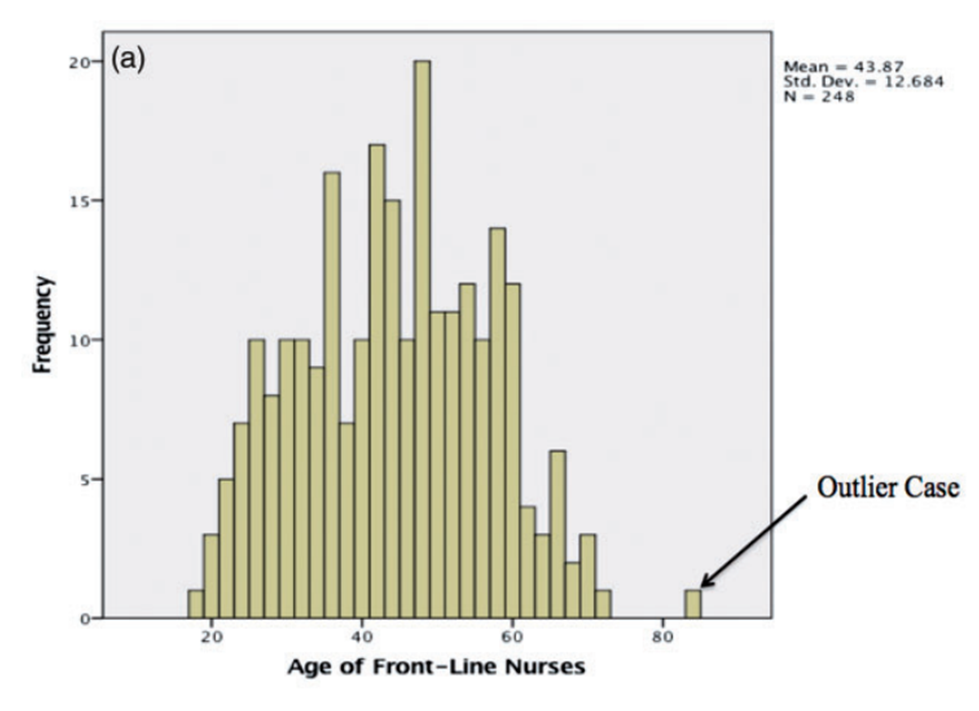
Adapted from Mowbray et al. (2019), p. 33.
Outliers make significant contributions to the understanding of various phenomena. Leys et al. (2019) propose a two-step process to address outliers in any research endeavor. Firstly, researchers must always strive to detect possible outliers using reliable quantitative tools. Secondly, researchers must decide how to address outliers by either keeping, recoding, or removing them from the dataset using qualitative information (Leys et al., 2019). It should be noted that bias is inadvertently introduced in the results if the detection and management procedures are conducted post hoc in a bid to select a modality that yields a desired outcome.
There are multiple options that are available for the management of outliers. I agree with Leys et al. (2019) that one should ask judges, such as colleagues or interns, who are blind to the study hypotheses to decide whether outliers that do not correspond to selection criteria should be included. The process must be conducted before further data analysis. To maintain credibility, the second proposed solution is to stick to the pre-registered decision regardless of other arguments. Error outliers can be removed from the sample provided the process is relayed transparently (Gibbert et al., 2021). The impact of outliers on research findings must not be ignored. The seemingly misplaced data points play a critical role in advancing the science of social work because they contextualize phenomena in ways that could lead to the discovery of novel theoretical perspectives.
The handling of outliers when conducting disparities-related research is critical. The oppressed, marginalized, and vulnerable populations correspond to the notion of outliers because the correct interpretation of data and the resultant programs is essential for fulfilling all their needs. It is worth considering that outliers may result from measurement errors, chance variations, or true heterogeneity in a given dataset. When conducting research on oppressed, marginalized, and vulnerable populations, it is vital to ascertain whether the outliers result from true heterogeneity by analyzing any systematic patterns in the extreme values. In the event outliers result from true heterogeneity, they could be interesting. Interesting outliers have significant implications for oppressed, marginalized, and vulnerable populations because they could represent specific realities such as extremities of marginalization, severe vulnerability, or a high degree of oppression. Identifying why outliers exist in these populations could help identify essential phenomena in disparities research. Interesting outliers in oppressed, marginalized, and vulnerable populations represent a critical sub-population that requires careful analysis to ascertain the factors contributing to poor outcomes. The consideration of extreme values is important because they represent opportunities for developing effective interventions for vulnerable sub-populations.
The advancement of the social sciences depends on the proper application of scientific principles and methods of inquiry. Statistics contribute immensely to this endeavor because they facilitate the extraction of meaning from large chunks of quantitative data. This allows practitioners to formulate theories and create interventions that significantly impact society. Outliers must be included in results because they often represent sub-populations that may provide insight into previously unknown phenomena. Moreover, outliers may represent specific realities that, if ignored, may leave critical social problems unchecked. Statistics plays a crucial role in explicating phenomena and addressing some of society's most pressing challenges.

Comments